Ever wondered why the symptoms of candida albicans overgrowth and alcohol intoxication or a hangover are so similar?
Many may not realize it but there is an overlap of symptoms caused by a compound that joins these two together in some respects.
Think about it. Symptoms of:
- Brain fog
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Silly behaviour or ‘giddiness’
Sure, there are many possible reasons for the above symptoms, but you may even use the analogy of having a ‘drunk child’ when trying to explain the symptoms of candida overgrowth in children to parents. Of course it doesn’t mean your child is drunk, but there is a chemical substance responsible for this type of behaviour and symptoms in both scenarios.
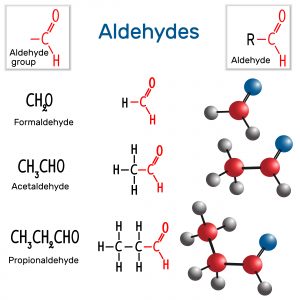
ACETALDEHYDE
Acetylaldehyde is a by-product of candida and alcohol metabolism and is responsible for the hangover feeling you get after a night out, or die-off reactions from yeast kill-off. Some people have a great ability to detoxify this substance, whilst others are super-sensitive to all kinds of aldehydes including those found in paints, perfumes and formaldehyde from new furniture gassing off.
Aldehydes are highly toxic if they are not cleared via normal detoxification systems and can cause irreversable mitochondrial damage. As mentioned they are found in chemical compounds (especially paints and perfumes), alcoholic beverages, and produced by the fungal organism candida albicans.
Some of its other effects on your biochemistry include:
- Binding and inactivating glutathione – this reduces the clearance of many other toxins
- Impairs the function of lymphocytes and red blood cells
- Increases adrenaline release – heart palpitations and anxiety
- Dilates blood vessels in the brain – headaches
- Multiple Chemical Sensitivity – if exposed on chronic basis
- Binds to dopamine – affects mood and hunger signals
SHORT-CHAIN vs LONG-CHAIN ALDEHYDES
When aldehydes have long side chains it makes it harder for this compound to dissolve in water and thus enter through cell membranes. This makes long-chain aldehydes less toxic than short-chain aldehydes.
ALDEHYDE DEHYDROGENASE (ALDH)
This family of enzymes are responsible for breaking down acetylaldehyde into acetic acid which is harmless and easily removed form the body.
Downregulation of these enzymes will cause toxic effects of aldehyde build-up and upregulation will increase stress adaptation and tolerance. This enzyme needs NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) as a cofactor but is also upregulated with alpha lipoic acid (ALA) and needs vitamin B1 or thiamine to function properly.
Vitamin B1 or thiamine transporters (THTR-1 and THTR-2) are down-regulated by high blood glucose and more vitamin B1 is lost through the kidneys via urine. This means a high sugar intake or conditions like diabetes will affect how well we absorb vitamin B1.
Metabolic Syndrome and Fatty Liver
This is a problem because alcohol is often combined with high sugar drinks (think bourbon and coke, mixer drinks, alcopops, etc.) and candida thrives in a high sugar environment. A lot of acetylaldehyde is produced in both these scenarios, but clearance of it can be slowed due to poor vitamin B1 absorption.
ALCOHOL AND BLOOD SUGAR
Studies have shown that the intake of alcohol in those with ALDH2 deficiencies can have a worsening of blood sugar problems. This is associated with diabetes, increases in HbA1c or neural damage brought on by excess glucose in the blood stream.
Acetylaldehyde has also been shown to upregulate G6PDH by up to 40%. G6PDH enhances glucose conversion to Glucose-6-phosphate. After this conversion glucose cannot leave the cell as it is an irreversable reaction. You can read more about this in the article Metabolic Syndrome and Fatty Liver.
FORMALDEHYDE
This is not acetylaldehyde, but being an aldehyde I am including it here.
When there is a lack of methylation, histones will start to demethylate which allows genes to start transcribing in order to make products. Formaldehyde is released by the body during this process. So, poor methylation can result in unhealthy or unbalanced formaldehyde production which may be toxic to the mitochondria and affect its ability to make ATP/energy for all the cells in the body.
Formaldehyde (bifunctional) is also much more toxic than acetylaldehyde (monofunctional). Look at the difference in chain lengths between them as well in the image further above.
ALPHA LIPOIC ACID
Alpha lipoic acid has been found to bind to excess aldehydes, reduce aldehyde production and increase aldehyde excretion.
MOLYBDENUM
This mineral is involved in acetylaldehyde clearance but also in sulfite clearance via SUOX (Sulfite Oxidase) and uric acid synthesis via XO (Xanthine Oxidase). Those who are deficient in molybdenum are often sensitive to the amino acid methionine but do better with cysteine or taurine.
IN SUMMARY…
There are common links and common symptoms between candida albicans overgrowth, multiple chemical sensitivities and too much alcohol. The main compound responsible for this is acetaldehyde and other aldehydes, and the enzymes/genes involved here that would need support include ALDH (Aldehyde Dehydrogenase) and ADH (Alcohol Dehydrogenase).
Vitamin B or thiamine deficiency and blood sugar imbalances should be considered, but candida overgrowth needs to be dealt with if present.
You can test for candida overgrowth and thiamine deficiencies through an Organic Acid Test.
References:
Acetylaldehyde oxidation in molybdenum deficiency





I’ve suffered for 6 years from Multiple Chemical Sensitivity. It became prevalent after being exposed to high levels of aspergillus mold for months at work in 2014. I ‘ve always been a moderate drinker but drank more due to the mold to relieve my allergic reactions. Once away from mold I continued to drink and then became extremely allergic to everything and everyone, I was nicknamed bubble boy. Cleveland Clinic tested me for everything environmental and chemical in 2015. The chemical patch test had 6 extreme readings which shocked the Dr. Long story short, I stopped drinking due to worsened anxiety after Covid only to now discover my allergies/sensitivities have cleared, nigh time headaches have cleared, airways are cleared, anxiety much better, gastro issues gone, insomnia not so bad. I never realized all these life changing ailments seem to be due to an intolerance to alcohol. This article is the first time I’ve read there is this alcohol related connection to all of my medical issues. Everything makes sense now, everything you wrote that I mentions on not spoke directly to me. Thank you for connecting the dots,
Hi Tomas, I’m so glad you finally got the answers you needed and that you have quality of life back :).
correction “everything you wrote the I mentioned or not spoke directly to me”